enee.io – Powering efficiency: Resolving overcharging challenges for sustained savings (Nigeria)
Who, What & Where
- enee.io
- enee.io system
- Lagos, Nigeria
The Company
Executive Summary:
enee.io, an energy monitoring system provider, conducted a trial to help a prestigious Nigerian company optimise a 48V battery bank at a bank branch in Lagos, which consists of 24 x 2V 1000ah VRLA cells. enee.io’s analysis revealed moderate issues affecting the battery bank’s performance and longevity. The primary concern was the overcharging of batteries, leading to dry-out and a subsequent reduction in their lifespan. This report outlines the negative effects, potential consequences, mitigation steps, and the considerable savings achievable by implementing enee.io’s recommendations.
The challenge
Key Information:
The battery bank was newly installed in August 2023, making the battery bank just over 5 months old.
Based on total energy throughput per day the battery bank is completing 1.2 discharge cycles per day.
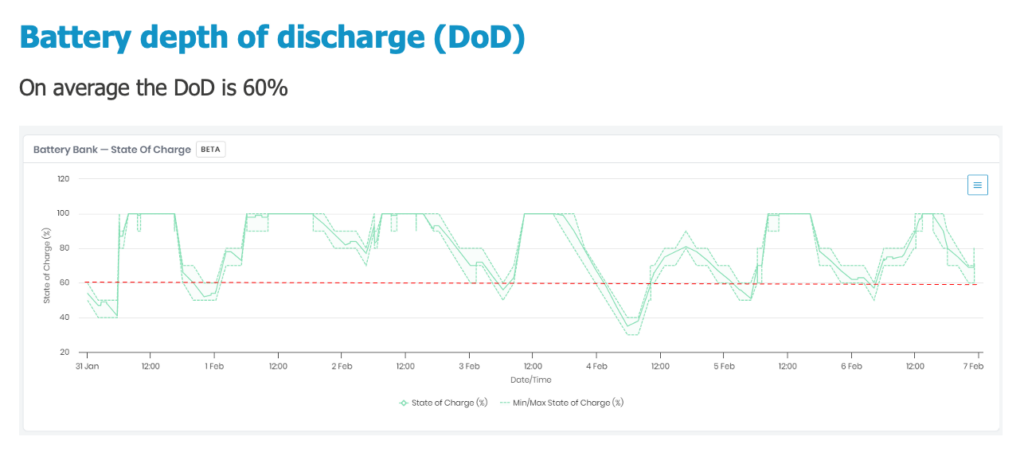
The average depth of discharge was 60% and the average operating temperature of 30degC.
Based on the above criteria the battery is designed to last 2100 cycles, which is 1740 calendar days at 1.2 cycles per day.
Overcharging of Batteries:
The current charging practices were causing overcharging of the battery bank. Overcharging of a VRLA battery leads to increased battery temperature, dry out of the VRLA batteries and excessive energy consumption. This jeopardizes the health and lifespan of the battery bank and increases energy costs.
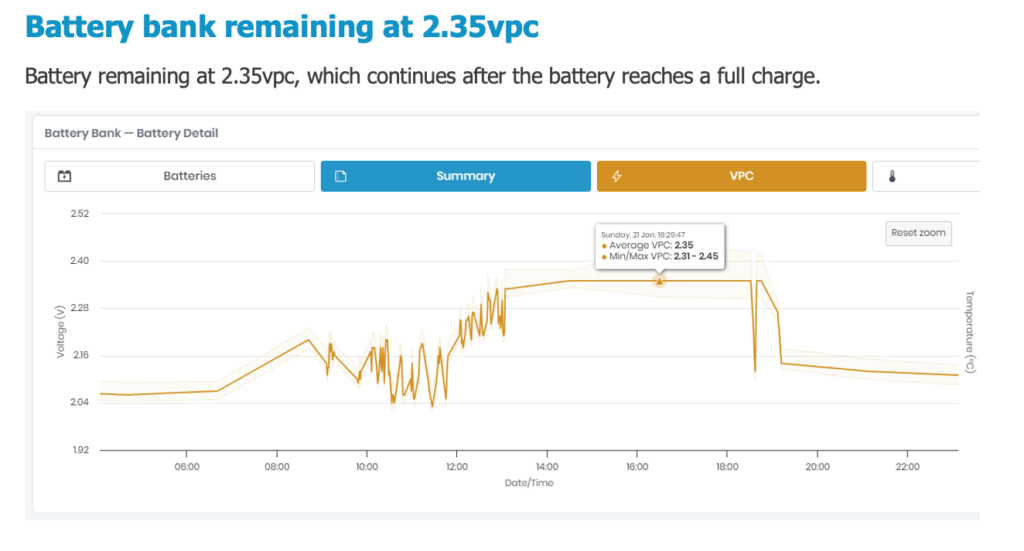
During charge, the battery bank reached a maximum of 2.35vpc (56.4v), which it then remained at indefinitely, even after the battery became fully charged.
It is expected to see a drop in the charge voltage to float charge, which would be around 2.25vpc (54v) until the battery starts to discharge.
The prolonged period of charge at 2.35vpc results in excessive energy being put into the battery after reaching full charge, resulting in increased heating of the battery and a loss of energy.
Technical Consequences of Overcharging:
Overcharging a Valve Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) battery has several detrimental consequences, impacting the performance, lifespan, and safety of the battery. Here are the key consequences of overcharging a VRLA battery:
Reduced Battery Life:
Overcharging accelerates the aging process of the battery by causing excessive heat, which leads to the degradation of internal components. This results in a significant reduction in the overall lifespan of the VRLA battery.
It was estimated that the battery bank would be at end-of-life in 2.1 years, compared to 4.0 years if issues were resolved.
Thermal Runaway:
Overcharging increases the internal temperature of the battery. If this heat is not dissipated effectively, it can lead to thermal runaway—a self-reinforcing reaction causing further temperature increase. This can result in the release of hydrogen gas, electrolyte leakage, and, in extreme cases, the risk of explosion and fire.
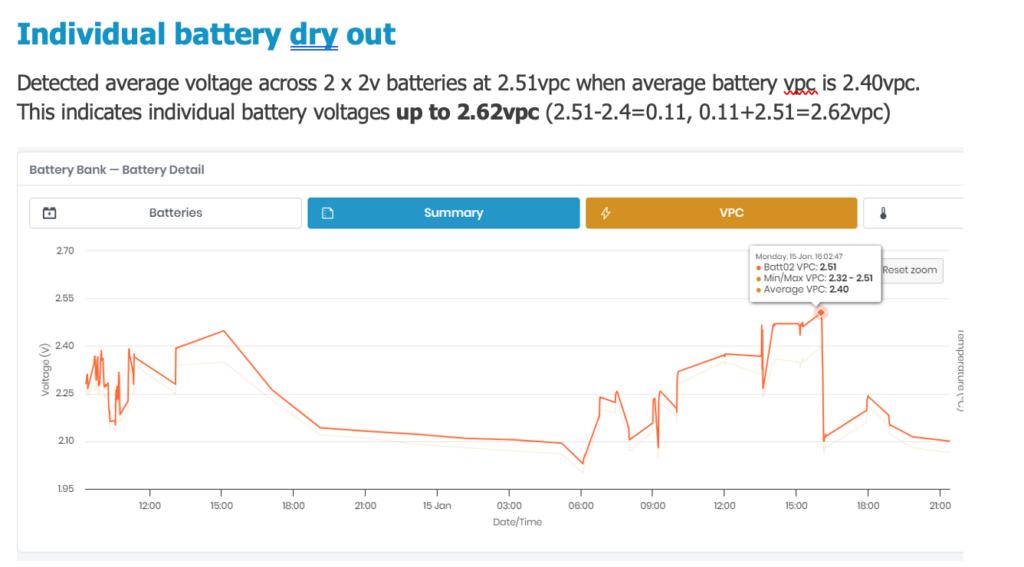
Dry Out and Water Loss:
Overcharging causes electrolysis, leading to the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. This process results in water loss, leading to the drying out of the battery. A dry battery loses capacity and may become irreversibly damaged.
Plate Corrosion:
The increased production of oxygen during overcharging can cause corrosion of the positive plates. Corroded plates result in increased internal resistance, reduced capacity, and compromised overall battery performance.
Increased Maintenance Costs:
Overcharging necessitates more frequent maintenance, including monitoring water levels, replenishing lost water, and replacing damaged batteries or components. These additional maintenance requirements contribute to higher operational costs.
Environmental Impact:
Overcharging can lead to premature failure and disposal of batteries, contributing to the environmental impact of end-of-life batteries.
Reduced Efficiency:
Overcharged batteries become less efficient in storing and delivering energy. This reduced efficiency results in more frequent charging cycles and increased energy consumption.
Increased Energy Costs:
We have calculated that 6.2kWh of energy is lost per day due to overcharging of the battery bank, equating to increased diesel consumption of 2.5ltrs per day.
Renewable Solution
Mitigation Steps:
To address the overcharging issue from a technical perspective, we recommended the following mitigation steps:
Voltage Regulation:
Check the battery charging voltage settings and adjust, ensuring they align with the manufacturer’s specifications and prevent overcharging.
Ongoing Monitoring:
Once mitigation steps have been taken, battery performance data will be reviewed to assess impact of changes, with further recommendations provided if necessary.
Savings Calculation:
Based on our technical analysis, corrective actions will result in substantial savings:
Extended remaining battery life from 2.1 to 4.0 years.Estimated saving of $4.64 per day.
Savings based on:
- Amortised CAPEX cost of $375USD per 2v battery and $9,000 for the entire 48v battery bank.
- Predicted battery life when new of 4.8 years, based on 60% depth of discharge at 30degC and 1.2 cycles per day.
- Estimated remaining life 4.0 years if issues resolved.
- Remaining life at current level of deterioration 2.1 years.
Reduced energy requirements resulting in reduced diesel spend.
Estimated saving of $2.48 per day.
Savings based on:
- Energy discharged from battery bank per day 40kWh
- Expected efficiency when new 90% = 44.4kWH expected charge energy
- Measured actual efficiency 79% = 50.6kWh actual charge energy
- Excess charge energy = 50.6-44.4 = 6.2kWh per day
- Cost of charge per kWh = $0.40 per kWh based on cost of charge from DG
- Lost energy per day = $0.40 x 6.2kWh = $2.48USD
Total Savings:
Extended battery life $2.48 + Energy savings $4.64 = $7.12 per day
Project Financing and Costs
Return on Investment (ROI):
Implementing the enee.io system comes at a cost of $340 USD, this includes the hardware cost and 1st year subscription.
Providing a remarkable ROI of just 48 days.
Project Outcome
Addressing the technical consequences of overcharging identified through the enee.io system will not only optimise operational efficiency but also significantly reduce operational costs and enhance the overall reliability of the power system. We recommended immediate action to implement the proposed technical mitigation steps for prolonged battery life and sustained savings.
In order to simplify the report, we have focused on the 2 key cost considerations, reduced battery life and increased diesel consumption. There are additional costs that could be considered, such as increased DG maintenance, disruption due to system breakdown, administration and operational costs in replacing a battery.
enee.io has over 30 proprietary algorithms that continuously run on the data collected from our IoT sensors. The issue identified from the trial is just one example of the insights and potential savings that can be gained from the enee.io energy monitoring system.